Light, reparable bullet-proof armour developed
Scientists have developed a new transparent bullet-proof armour that is lighter in weight and can easily be repaired on the…
Polymers have a wide variety of industrial and commercial uses such as in making grocery bags, soda and water bottles, textile fibers, phones, computers, food packaging, auto-parts, toys, etc.
(PIB)
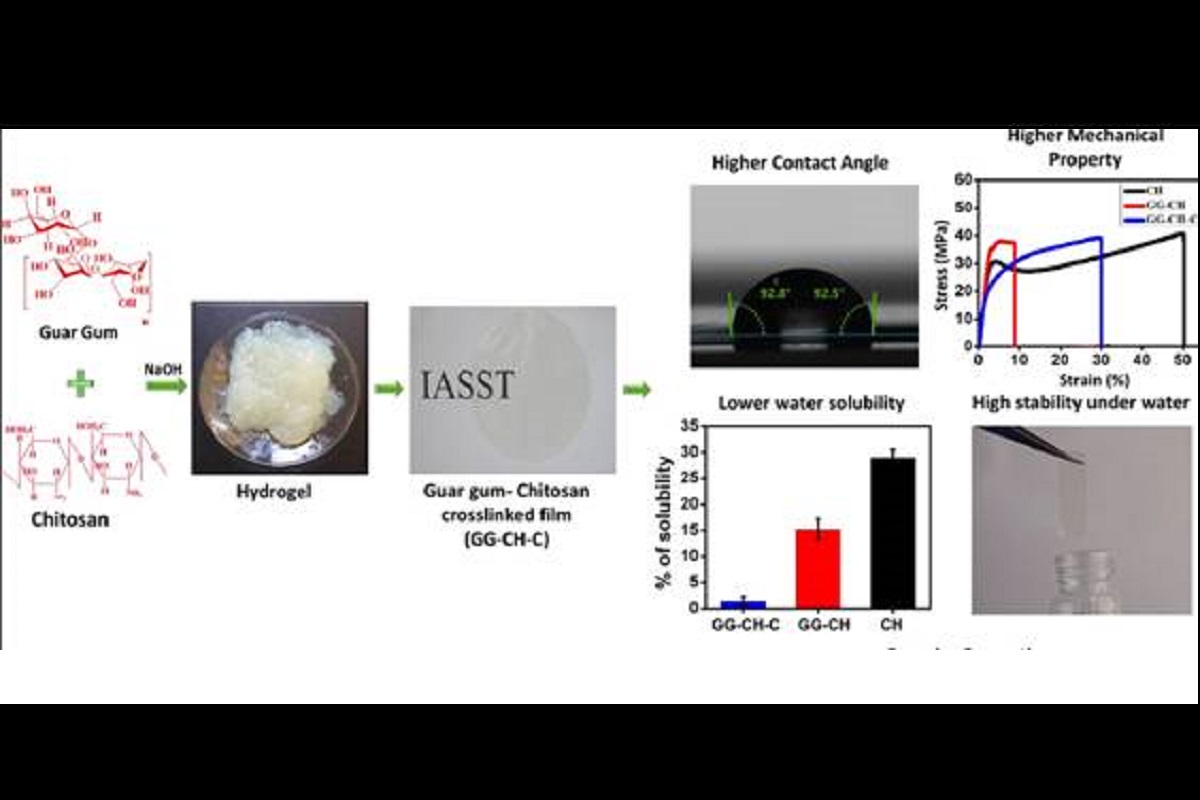
In a development that is likely to help effectively deal with the menace of piling non-biodegradable packaging materials, including water and soda bottles, Indian scientists have developed a biodegradable polymer using seeds of guar beans and shells of crab and shrimps.
Polymers have a wide variety of industrial and commercial uses such as in making grocery bags, soda and water bottles, textile fibers, phones, computers, food packaging, auto-parts, toys, etc. The problem with the polymer is that it is not biodegradable and hence poses a major challenge to the environment and earth’s ecosystem.
The newly developed environmentally friendly, non-toxic, biodegradable polymer using guar gum and chitosan, extracted from guar beans and shells of crab and shrimps, have ‘high water stability, high mechanical strength, and excellent resistance to harsh environmental conditions’ which can potentially be used in packaging applications, according to a Ministry of Science and Technology note here.
Advertisement
Polysaccharides extracted from guar beans and shells of crab and shrimps is one of the biopolymers with high potential for use in synthesis of packaging material. However, due to some drawbacks of polysaccharides, such as low mechanical properties, high water-solubility, and low barrier properties, they are not preferred.
“In order to overcome these challenges of polysaccharide, Dr Devasish Chowdhury, Associate Professor, and Sazzadur Rahman, Inspire Junior Research Fellow, fabricated a guar gum-chitosan composite film which is a cross-linked polysaccharide without using any plasticizer with the help of a method called the solution casting method (a simple technique to make polymer films),” the ministry note said.
“The fabricated biopolymer composite film had high water stability, high mechanical strength, and excellent resistance to harsh environmental conditions. This work has been published recently in the journal ‘Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications,” according to the ministry.
The researchers have found that the fabricated cross-linked film did not dissolve in water even after 240 hours. Besides, the mechanical strength of cross-linked guar gum-chitosan composite film was found to be higher compared to general biopolymer (biopolymer are known to have poor strength) and highly water repellent or hydrophobic due to its high contact angle of 92.8º. It has also low water vapor permeability when compared with the film made only from chitosan, researchers said.
Advertisement